When traffic moves between two roads that are at the same grade, these connecting segments are not technically ramps to Waze (unless it falls into one of the Exceptions listed below, which are not present on the Rwandan network of 2023). How to handle these connectors depends on the exact situation.
Should the connector be mapped?
First and foremost, the need to have the connector mapped needs to be established. As the driver approaches an intersection, Waze has usually given at least one warning that a turn is imminent, and we can assume that the driver is already looking for turn lanes. For most intersections, that is enough to guide the driver into the proper lane and to turn at the proper time; in other words, it is enough that the two roads intersect without separately mapped turning lanes.
There are only a few situations in which connectors are called for in an intersection:
- When the turn lane physically separates from the main road well in advance of the intersection, i.e., where the point of divergence (the "theoretical gore") is more than a couple car lengths before the stop line of the main lanes of traffic.
- When the turn lane is far enough from the point of intersection on the map (due to the size of the intersection or the angle at which the roads meet) that the driver might overshoot while waiting for a delayed "turn" audible, or that the Waze client might become confused and disrupt navigation. For such case, you should try to take the intersection yourself with the client, or many URs complaining about the indication at the intersection arise.
Consider the addition or removal of at-grade connectors carefully. Connectors can bring the map closer to reality, but they can also add to your workload when the time comes to check connectivity, direction, name, etc., and make it impossible for heuristics to work on lanes at # or H intersections.
When in doubt, discuss it within the community or leave it out!
Road type

Although sometimes referred to as ramps, to Waze these are not ramps. The Ramp road type in Waze should only be used for situations where two roadways have a grade separated intersection (in Rwanda, typically at Flyovers entry/exit) or if the situation matches one of the Exceptions listed below.
The connector segment's type should be set based on the lowest of the types of roads it connects, as in the following examples:
- Street to Minor Highway should be Street type.
- Minor Highway to Primary Street should be Primary Street type.
- Primary Street to Primary Street should be Primary Street type.
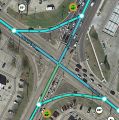
In the example image on the right, note how the top-left quadrant of the intersection does not have a connector mapped because it does not meet the requirement of being significantly separated from the main intersection.
Road name
In most cases, checking None for the Street name will be sufficient. Navigation instructions will simply use the name of the next segment to which the connector segment connects.
If there are specific signs at the intersection which are confusing or contrary to the destination road segment name, then a name can be applied to the connector.
Geometry and turn instructions
Turn replacement AGCs
The "typical" at-grade connector takes the place of a normal turn instruction at an intersection, giving the same turn instruction at the point when the driver enters the AGC, and giving no instruction as the driver exits the AGC. In the typical turn replacement AGC, the turning motion made by the driver is more or less consistent throughout the AGC, beginning at the gore point.
Turn replacement AGCs should be mapped starting at the gore point that separates the AGC from the main lanes of traffic.
-
Typical turn replacement AGC
-
Turn replacement AGCs start at the gore, not at the solid white line
-
Typical turn replacement AGCs
-
Turn replacement AGCs start at the gore, not at the solid white line
Long lead AGCs
These type of AGCs are not present in Rwanda in 2023. This is for information only, and/or if road infrastructure evolution required it.
On some AGCs, the actual turning motion starts well after the gore. After entering the AGC, the driver's path is more or less straight for some time before the motion of the turn itself begins.
Like turn replacement AGCs, long lead AGCs should be mapped starting at the gore point that separates the AGC from the main lanes of traffic.
To better represent the actual motions involved, long lead AGCs should be configured with an instruction to "keep right" or "keep left" onto the AGC and, where needed, a second instruction (often "turn right" or "turn left") given as the driver exits the AGC.
-
The painted gore separates the AGC from traffic well before the left turn motion begins
-
The raised grassy area separates the AGC from traffic well before the left turn motion begins
-
The painted gore creates an AGC which is in many ways similar to a freeway exit ramp
The long-lead AGC configuration provides an additional benefit for left turn lanes where U turns are allowed by allowing the 2nd instruction in the two-instruction set to be "make a U turn" on the U turn path.
Turn restrictions

Connectors, if simply added to the map and all turns were allowed, would cause significant routing challenges, especially between two 2-way roads. Divided roadways have their own challenges, but turn restrictions, due to the 1-way nature of the main segments, are simpler.
In Rwanda, a simple right-turn connector between two 2-way streets, requires that the right turn be restricted at both the primary intersection, and at the connector itself so Waze will not be allowed to tell the driver to turn left across the road to get onto the connector.

AND, at the end of the connector, the left turn must be restricted:

The danger in that if you enable the "show all restricted connectivity arrows" function in the editor at this intersection, you can see there are many restricted turns. This is sometimes a target for someone looking to remove all restricted turns by abusing the use of the 'w' or Allow All turns function. This is of course something NOT to do!
Speed Limit
AGCs follow these 3 basic rules in this order of preference (apply first match):
- If it has its own dedicated posted regulation SL, use it.
- If the SL before and after are the same, use it
- Use the SL of the segment feeding into the AGC (s-in)
Exceptions
All those exception are NOT present in Rwanda as of 2023. This is for information only, and/or if road infrastructure evolution required it.
Median U turn intersection (MUTI)
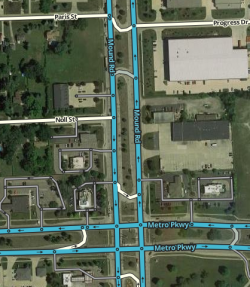
The median crossing segments in a median U turn (aka "Michigan left") intersection should be set to the RAMP type.
Restricted crossing U turn (RCUT) intersection
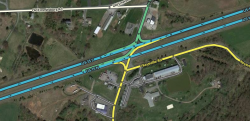
The median crossing segments in a restricted crossing U turn (aka "J turn" or "Superstreet") intersection should be set to the RAMP type.
Displaced left turn (DLT) intersection

The crossover left turn lanes and the resultant elongated right turn lanes in a displaced left turn (or "continuous flow") intersection should be set to the RAMP type.
Jughandle

Jughandle segments should be set to the RAMP type.
Signed, numbered exit

Example: Garden State Parkway Exit 10 in Cape May Court House, New Jersey, USA.
The Garden State Parkway is mostly a freeway class toll-road that runs north/south through New Jersey. As the Parkway approaches its southern terminus, the number of lanes is reduced, and at-grade intersections with signed, numbered exits are interspersed with controlled access sections using grade-separated ramps.
In order to produce an instruction to Exit Right for the at-grade intersections, rather than Keep Right or Turn Right, we must use a junction angle of less than 45 degrees and a connector segment of a road type other than Freeway or Highway. Ramp type is ideal for this application because it does not display road names in the app. Segments for numbered exits are named to produce specific visual and TTS instructions, rather than by standard rules for at-grade connectors, and it would be inappropriate to display such names on the map.